Huawei calls for ‘favourable policy’ and cross-sector collaboration to speed up 5G development

At the 10th annual Mobile Broadband Forum (#MBBF) held today in Zurich, Huawei‘s deputy chairman Ken Hu described the current status of 5G development around the world. In addition to highlighting the value 5G has already brought to consumers and industries in early adopter countries, he also delved into the importance of favourable policy and cross-sector collaboration for speeding up the next stage of 5G development.
“We’ve made great progress,” says Hu. “But to make the most of 5G, we need to work together to deal with the real challenges that lie ahead: spectrum, site resources, and cross-sector collaboration. 5G is not just faster 4G. It will play a completely different role in our lives, so as an industry, we all need to have a fresh mindset to drive its future development.”
5G is speeding up around the world
Less than a year since standards were frozen, 5G networks have already seen large-scale commercial deployment, much faster than 4G. Thus far, carriers in more than 20 markets have launched a total of 40 commercial 5G networks, and more than 60 are expected by the end of the year.
5G is supercharging user experience. In South Korea, the first market to launch a commercial 5G network, local carriers have signed up more than 3.5 million 5G subscribers in under six months. Much of this growth can be attributed to new services like 5G-powered augmented/virtual reality (AR/VR) and live 360º HD sports broadcasting. With these services alone, data consumption among early 5G adopters has increased by a factor of three, up to 1.3 gigabytes per month.
Beyond growing data consumption, carriers are seeing more revenue streams as well. For example, South Korean carrier LG U+ released 5G-powered VR/AR services as part of its premium data plans. In just three months since the 5G launch, the proportion of premium subscribers grew from 3.1% to 5.3%.
Different industries are also deriving new value from the first round of industrial 5G applications. “5G applications for enhanced mobile broadband, entertainment, and manufacturing are already here,” adds Hu. “We can’t say for sure what type of applications we’ll see in the future, but right now it’s clear that every single industry will benefit from 5G technology.”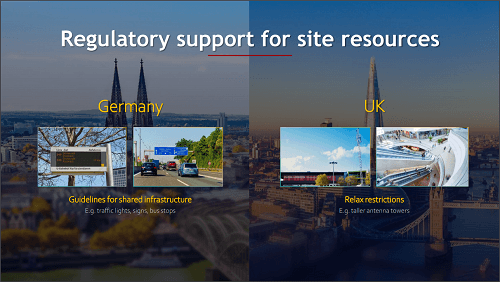
Favourable policies for spectrum and sites
Hu notes that spectrum resources, specifically the cost and availability of spectrum, are one of the most significant barriers that carriers face in the future. “We hope governments can provide more spectrum resources to carriers, and consider more flexible pricing models. This will reduce the initial CAPEX burden on carriers as they roll out their 5G networks.”
Hu also recommends that governments start actively planning to meet new spectrum demand over the next five to 10 years, noting that 6GHz spectrum bands are a good starting point.
“Our industry also needs more support for site resources,” Hu continues. “Costs are still too high, and site availability always falls short of demand. Regulators should step up and improve the situation by opening up more public infrastructure for sharing, and providing guidance on site construction.”
In Shanghai, for example, the city government has reportedly set standards for multi-functional utility poles. By the end of 2020, they will install these poles along 500 kilometres of public roads, which will be used to support 30,000 additional 5G sites. That’s an increase of 75% on the total number of mobile base stations currently built throughout the city.
In Europe, government ministries are working directly with carriers to identify shared use requirements for 5G sites and other forms of public infrastructure (such as traffic lights, signs, and bus stops) to drive down costs for everyone through infrastructure sharing.
Expanding cross-sector cooperation
At the end of his presentation Hu emphasises the importance of cross-sector collaboration. “We still have some challenges in terms of vertical industry knowledge, use cases, and business case development. So we need to innovate together. If we can have an open mind, work together with industry partners to identify real problems, and explore what works and what doesn’t, that will make it easier for us to unleash the power of 5G,” he adds.
In order to promote cross-sector innovation and greater regional collaboration, Huawei opened its first 5G Joint Innovation Centre for Europe, located in Zurich. The centre is a joint effort between Huawei and Swiss-based operator Sunrise. It will serve as an innovation platform that helps European companies work together across sectors and develop industry-specific 5G solutions.
“Every country has its own economic strengths. These are the areas we can focus on, and combine 5G technology with industry-specific solutions to enhance each country’s competitiveness,” Hu concludes.
This year’s Mobile Broadband Forum brings together more than 1,500 representatives from carriers, vertical industries, equipment manufacturers, standards organisations, analyst firms, and the media. The exhibition hall showcases 5G technology, commercial solutions, and an array of 5G applications for individual consumers, households, and businesses, including 5G-powered cloud AR/VR, 8K broadcasting, cloud gaming, machine vision, and 5G-powered remote control solutions.
Comment on this article below or via Twitter:
Recent Posts
- What Is an Exoskeleton Suit?
- Where can you use an ultrasonic motor?
- Smart Camera: System That You Can Use for a Wide Variety of Purposes
- Why Is the Smart Toothbrush Better Than a Regular One?
- Microcontrollers: An Integral Part of Embedded Hardware
- Air Quality Monitoring System: Why It’s So Important in Modern Realities

